A) help to keep prices down.
B) help to prevent a single firm from acquiring ownership of a key resource.
C) encourage creative activity.
D) discourage the production of inefficient products.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following formulas would correctly calculate a monopolist's profit?
A) profit = price - marginal cost
B) profit = price - average total cost
C) profit = (price - marginal cost) × quantity
D) profit = (price - average total cost) × quantity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 15-8
The following table provides information on the price, quantity, and average total cost for a monopoly. 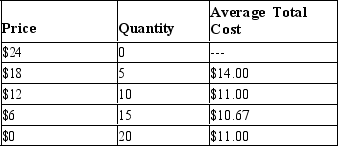 -Refer to Table 15-8. At what price will the monopolist maximize his profit?
-Refer to Table 15-8. At what price will the monopolist maximize his profit?
A) $6
B) $12
C) $18
D) $24
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a monopolist is able to sell its product at different prices, it is engaging in
A) distribution pricing.
B) quality-adjusted pricing.
C) arbitrage.
D) price discrimination.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The fundamental cause of monopoly is
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose ABC Aluminum Inc. owns 80% of the world's bauxite, a mineral used in the production of aluminum. Which of the following reasons describes the fundamental barrier to entry for the aluminum industry?
A) monopoly resources
B) government regulation
C) the production process
D) Both a and b are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A natural monopoly occurs when
A) the product is sold in its natural state, such as water or diamonds.
B) there are economies of scale over the relevant range of output.
C) the firm is characterized by a rising marginal cost curve.
D) production requires the use of free natural resources, such as water or air.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose most people regard emeralds, rubies, and sapphires as close substitutes for diamonds. Then DeBeers, a large diamond company, has
A) less incentive to advertise than it would otherwise have.
B) less market power than it would otherwise have.
C) more control over the price of diamonds than it would otherwise have.
D) higher profits than it would otherwise have.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a characteristic of a natural monopoly?
A) Fixed costs are typically a small portion of total costs.
B) Average total cost declines over large regions of output.
C) The product sold is a natural resource such as diamonds or water.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a monopolist reduces the quantity of output it produces and sells, the
A) price of its output increases.
B) price of its output remains constant.
C) price of its output decreases.
D) profits for the firm always decrease.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A natural monopoly has economies of scale for most if not all of its range of output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 15-6
A monopolist faces the following demand curve: 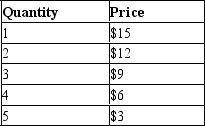 -Refer to Table 15-6. Suppose the monopolist has total fixed costs equal to $5 and a variable cost equal to $4 per unit for all units produced. What would the total profit be if she charged $6 per unit for her product?
-Refer to Table 15-6. Suppose the monopolist has total fixed costs equal to $5 and a variable cost equal to $4 per unit for all units produced. What would the total profit be if she charged $6 per unit for her product?
A) $1
B) $3
C) $8
D) $15
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15-8 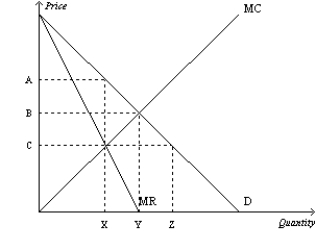 -Refer to Figure 15-8. What is the socially efficient price and quantity?
-Refer to Figure 15-8. What is the socially efficient price and quantity?
A) price = A; quantity = X
B) price = B; quantity = Y
C) price = B; quantity = X
D) price = C; quantity = X
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reason to regulate utilities instead of using antitrust laws to promote competition is that a utility is usually a
A) profit-maximizing monopoly.
B) producer of externalities.
C) revenue-maximizing monopoly.
D) natural monopoly.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A movie theater can increase its profits through price discrimination by charging a higher price to adults and a lower price to children if
A) adults buy more popcorn than children.
B) the cost of showing a movie to children is less than the cost of showing a movie to adults.
C) it has some degree of monopoly-pricing power.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Name brand drugs are able to continue capitalizing on their market power even after generic drugs enter the market because
A) (i) and (ii) only
B) (ii) and (iii) only
C) (i) and (iii) only
D) (i) , (ii) , and (iii)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 15-6
A monopolist faces the following demand curve:  -Refer to Table 15-6. Suppose the monopolist has total fixed costs equal to $5 and a variable cost equal to $4 per unit for all units produced. What is the profit-maximizing price?
-Refer to Table 15-6. Suppose the monopolist has total fixed costs equal to $5 and a variable cost equal to $4 per unit for all units produced. What is the profit-maximizing price?
A) $6
B) $9
C) $12
D) $15
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The laws governing patents and copyrights
A) eliminate the need for firms to engage in research and development.
B) are intended to serve private interests, not the public's interest.
C) reduce fixed costs for firms that obtain them.
D) None of the above is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A monopolist produces where P > MC = MR.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Price discrimination is a rational strategy for a profit-maximizing monopolist when
A) the monopolist finds itself able to produce only limited quantities of output.
B) consumers are unable to be segmented into identifiable markets.
C) the monopolist wishes to increase the deadweight loss that results from profit-maximizing behavior.
D) there is no opportunity for arbitrage across market segments.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 361 - 380 of 637
Related Exams