A) more goods per person.
B) a higher quality of goods.
C) a wider variety of goods.
D) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Labor productivity growth is the growth rate of output
A) per person in the economy.
B) per worker in the economy.
C) for labor-intensive economies.
D) for the entire economy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 17.1 below to answer the questions that follow. 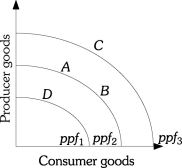 Figure 17.1
-Refer to Figure 17.1.An economic decline is represented by a movement from
Figure 17.1
-Refer to Figure 17.1.An economic decline is represented by a movement from
A) point A to point B.
B) point D to point A.
C) point C to point A.
D) point B to point A.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The aggregate production function is Y = 2K0.5L0.5.If there are 225 units of capital and 196 units of labor,aggregate output is
A) 420 units.
B) 508 units.
C) 700 units.
D) 842 units.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The relation between growth,as measured in ________,is an inverted U.
A) per capita income and pollution
B) income and expenditure
C) saving and investment
D) human capital and physical capital
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In Polynomia,real GDP increased by 8% and the population increased by 3% in 2012.In 2012,Polynomia experienced
A) economic growth,but not an increase in living standards.
B) economic growth and an increase in living standards.
C) no economic growth,but an increase in living standards.
D) an economic decline.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An important source of increasing productivity is
A) an increase in the ratio of capital to labor.
B) an increase in the ratio of labor to capital.
C) a decrease in the ratio of capital to labor.
D) faster growth in the labor force than in the capital stock.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mathematical representation of the technological relationship between inputs and national output is known as the
A) aggregate supply function.
B) production possibilities frontier.
C) aggregate production function.
D) input-output table.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A company uses 200 workers and 50 units of capital to produce 1,000 units of output.Its average labor productivity is
A) 4.
B) 5.
C) 20.
D) 25.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT an investment in human capital?
A) local governments begin providing free hepatitis vaccinations to any resident who wants one
B) the Precision Tool Company teaches all its workers how to repair all the machines in the factory
C) older workers return to school to update their skills
D) the Ferris Advertising Agency replaces its secretaries' typewriters with personal computers
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 17.2 below to answer the questions that follow. 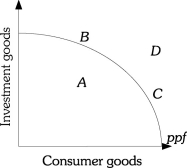 Figure 17.2
-Refer to Figure 17.2.Point ________ can not be produced by the people of this society.
Figure 17.2
-Refer to Figure 17.2.Point ________ can not be produced by the people of this society.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Human capital increases with on-the-job training.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As growth progresses and countries become richer,pollution
A) tends to fall.
B) rises exponentially.
C) rarely changes.
D) levels double.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 17.1 below to answer the questions that follow.  Figure 17.1
-Refer to Figure 17.1.Economic growth is represented by
Figure 17.1
-Refer to Figure 17.1.Economic growth is represented by
A) a movement from point D to point C.
B) a movement from point A to point C.
C) a movement from point D to point A.
D) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the capital stock
A) can increase output,even if it is not accompanied by an increase in the labor force.
B) provides valuable services directly,but not indirectly.
C) can increase output,but only if it is accompanied by an increase in the labor force.
D) cannot increase output,even if it is accompanied by an increase in the labor force.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An explanation for the "inverted U" is that increased industrialization and growth initially ________ the environment,and in the long run,environmental quality ________.
A) degrades;continues to get worse
B) improves;improves even more
C) improves;gets worse
D) degrades;improves
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Higher energy prices in the 1970s reduced labor productivity because
A) energy and capital are substitute inputs.
B) the rise in energy prices tended to push firms away from labor-intensive measures and toward more capital-intensive techniques.
C) a great deal of investment went into transforming the existing capital stock into more energy-efficient forms.
D) labor productivity has been lower when used with more capital-intensive techniques.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Zuliu Hu and Mohsin Khan have stated that the productivity gains in China over the past 20 years are,in large part,a result of market reforms from incorporating business into the public sector.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Technical change that results in a change in the production process is known as disembodied technical change.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Thomas Malthus and David Ricardo believed that to increase agricultural output,people would be forced to
A) farm land more intensively,in which case the returns to successive increases in population would diminish.
B) farm land less intensively,in which case the returns to successive increases in population would increase.
C) farm land more intensively,in which case the returns to successive increases in population would increase.
D) farm land less intensively,in which case the returns to successive increases in population would diminish.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 93
Related Exams